ESPRESSO science team on Twitter :
https://twitter.com/espresso_astro/status/1453274990124707840Today we present a new result of the @espresso_astro team which is one more example of how nature always has room to astonish us: 2 planets orbiting the same star in perpendicular orbits! A paper led by Vincent Bourrier
In most common planet formation scenarios, planets in a multi-planetary system are formed within a disk of gas and dust. After the disk dissipates, planets should then revolve their star in the same orbital plane, perpendicular to the stellar spin axis.
However, different mechanisms can disturb these orbital planes and make the planets orbit in mutually inclined orbits. Gravitational encounters between different bodies or the presence of massive outer companions in the system are some possibilities.
The star HD3167 was known to host three planets named HD3167b (a super-Earth with al ultra-short period of 23 hours), and the two mini-Neptunes HD3167d (with an orbital period of 8.5 days) and HD3167c (period of 29.8 days); discovered by @amvanderburg (see figure) and D. Gandolfi
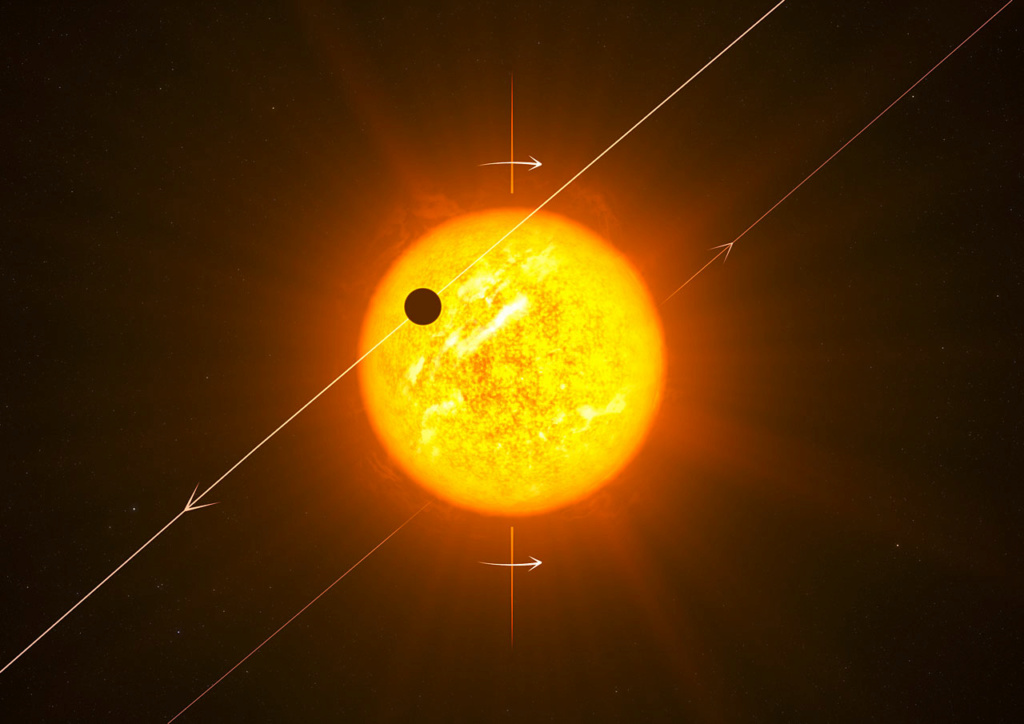
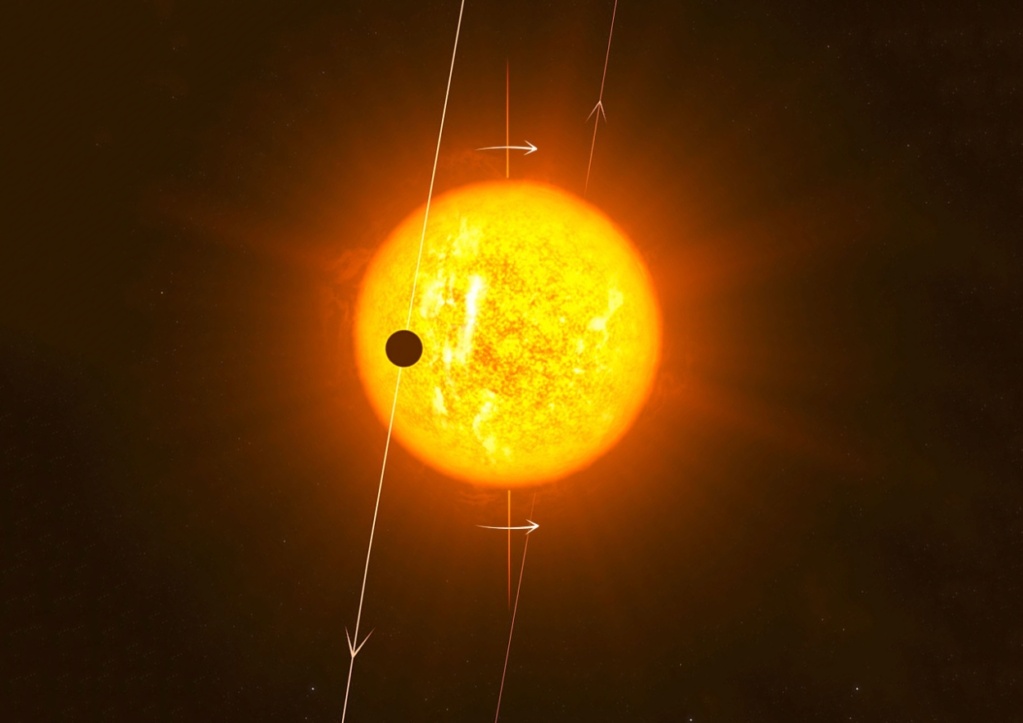
Surprisingly, the inner and the outer planets transit the star while the one in the middle (planet d) does not. Indeed, planet c was known to orbit in a highly inclined (polar) orbit wrt its star spin axis. This was already pretty shocking…
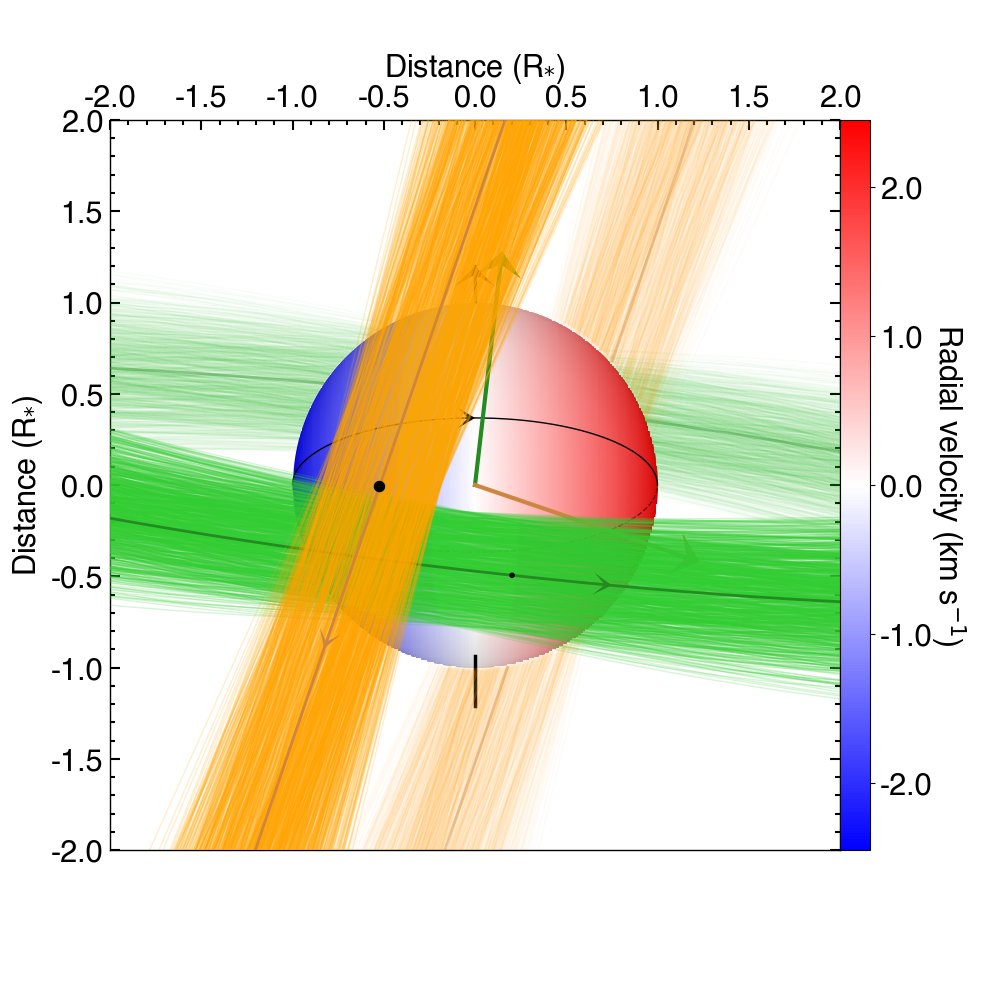
The above already indicated a complicated dynamical history for the system. So, why not going for it? That’s what we did. We focused on the very small inner planet (“b”) to uncover its relative orientation wrt to the other transiting planet (“c”).
We used @ESA_CHEOPS to refine the ephemeris of its transit time and ESPRESSO (@ESO) to measure its spin-orbit alignment. And guess what!? Planet “b” is perfectly aligned with the star and hence its orbital plane is perpendicular to that of planet “c”! A fully upside-down system!
This was a pretty challenging discovery because planet “b” is very small (only 1.7 times the Earth radius) so we had to develop the “Rossiter-McLaughling effect Revolutions (RMR) approach”. Check out the paper for details on this new technique:
https://aanda.org/articles/aa/full_html/2021/10/aa41527-21/aa41527-21.htmlThis result suggest this small planet is under the influence of its parent star keeping its primordial alignment, while the other two planets were severely influenced by an outer massive companion. Where is that companion? To be continued…
This work has been published in @AandA_journal
The Rossiter–McLaughlin effect revolutions: an ultra-short period planet and a warm mini-Neptune on perpendicular orbits